Probably, unless you already know this discipline well, when you hear the word "radiotherapy" this specialty comes to mind as a treatment for cancer, and you are not wrong, since it is one of the main and most effective techniques in the treatment of cancer. the dreaded neoplastic diseases.
Radiotherapy in medicine was discovered by physicist and Nobel laureate Marie Curie in 1898. Dr Marie Curie discovered the element Radium (atomic number 88) and combined it with X-rays discovered by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen in 1895, to create a type of medical treatment based on ionizing radiation that uses high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells. It has evolved so much until now that today great precision and minimal damage to healthy tissues is achieved, thanks to its application through large linear particle accelerators, known as LINACs.
But radiotherapy has advanced so much that it has been discovered that it is no longer only valid for treating cancer, but that it has other very powerful medical uses, and we will tell you about them here.
1) Keloid scar treatments
Keloid scars are a type of hypertrophic scar characterized by excessive growth beyond the boundaries of the original wound. They tend to be common after surgeries, burns or serious injuries, although there are people more genetically predisposed than others.
The main problem in the treatment of this type of scars is the ease for them to reproduce again, since they have a high capacity for regeneration by mitosis of their fibroblasts.
To eliminate these lesions, the excess scar is first removed with surgery and then radiotherapy is applied to prevent its reproduction. Radiotherapy acts on keloid scars by interfering with the process of formation and growth of scar tissue. By using low doses of targeted radiation, the activity of fibroblasts, the cells responsible for the production of collagen that forms scars on the wound, is reduced. In addition, radiotherapy helps to moderate the inflammatory response that accompanies the formation of these scars, so by limiting both cell proliferation and inflammation, it helps to flatten and soften the keloid scar, reducing its size and improving both the appearance and associated symptoms, such as itching or pain.

2) Trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic neurological condition characterized by intense, stabbing pain in the face, considered one of the most acute and debilitating pains a human being can experience.
This pain originates in the trigeminal nerve, which is one of the most important cranial nerves and is responsible for transmitting sensations from the face to the brain. Pain attacks can be triggered by everyday activities such as talking, eating, or even wind, and are often so severe and sudden that they are described as feeling like an electric shock. The intensity and frequency of these painful episodes can be so overwhelming that they significantly impact the patient's quality of life, leading to states of anxiety, depression and, in extreme cases, they can lead to suicidal thoughts or acts.
This condition, due to its devastating impact on the lives of those who suffer from it, requires careful and compassionate management, focused on both pain relief and the emotional and psychological support of the patient.
Stereotactic radiosurgery is used for radiotherapy treatment, specifically the technique known as Gamma Knife, which directs high-precision radiation beams to the trigeminal nerve at the location where it is believed to be compressed or irritated, usually near its origin in the brain.
This radiation is administered in a single high-dose session, and its goal is to selectively damage the trigeminal nerve root to block pain signals. The effect is not immediate, it may take weeks or even months for the patient to experience complete pain relief, but it offers a less invasive alternative to surgical procedures, with a faster recovery and fewer complications.
However, it is not free of risks and possible side effects, such as facial numbness or decreased sensitivity, so the decision to use it should be made after careful evaluation by specialists in pain management and neurosurgery.
3) Inflammatory diseases, such as plantar fasciitis or arthritis
Radiotherapy may also be effective in the management of certain non-malignant inflammatory diseases.
The underlying mechanism is based on the ability of low-dose radiation to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation; radiation acts by altering the functions of immune cells and decreasing the release of proinflammatory cytokines, which in turn reduces inflammation. and pain in the affected tissues. This approach is applied in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, certain types of tendinitis and bursitis, plantar fasciitis, and in skin disorders such as eczema and psoriasis.
In these diseases, the treatment is administered in much lower doses than those used for cancer treatment, thus minimizing the risks of side effects. In general, the use of radiation therapy for the treatment of inflammatory diseases is reserved for cases in which conventional treatments have been unsuccessful, given concerns about the potential long-term risks associated with radiation exposure.
4) Treatment of arteriovenous malformations
Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are congenital anomalies that result from abnormal development of blood vessels during fetal growth. These malformations affect the normal connection between arteries and veins, since the arteries connect directly to the veins without passing through the capillaries. This direct connection prevents the slow transfer of oxygen and nutrients that normally occurs in the capillaries.
When AVMs are located in the brain, symptoms may include headaches and/or seizures. In other parts of the body, symptoms may be less obvious, but often include pain or swelling.
The main risk associated with AVMs is bleeding, since the walls of the affected veins are weaker than those of the arteries and are not equipped to handle high blood pressure. This increases the risk of ruptures and bleeding, which can be serious and life-threatening, especially if the AVM is in the brain or spinal cord.
Treatment of AVMs, especially in the brain, can be done safely and effectively with a special type of radiation therapy called stereotactic radiosurgery, such as Gamma Knife treatment, as is the case with trigeminal neuralgia.
The goal is for the radiation to cause a reaction in the abnormal blood vessels that causes them to scar and close. This method is much less invasive than traditional surgery, which means less risk and discomfort for the patient and is especially useful for treating AVMs that are difficult to access surgically or that have a high risk of complications if treated with more invasive methods.
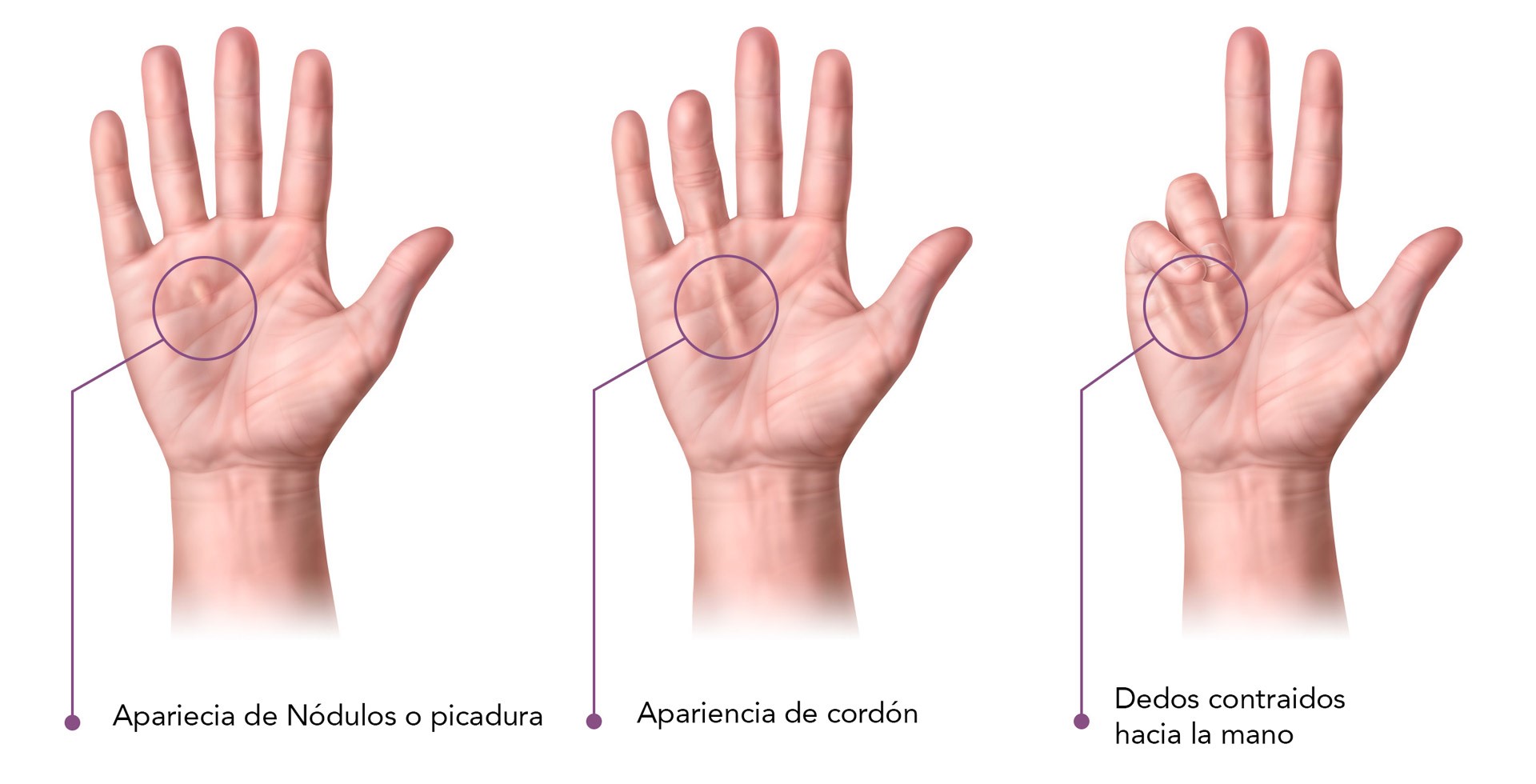
5) Dupuytren disease and Ledderhose disease
Dupuytren's and Ledderhose's diseases are very similar, as they both affect the fascia tissue, but they differ in their location: the first affects the hands and the second affects the feet. Both are characterized by the formation of nodules and fibrous bands that can be painful and make movement difficult. In the case of Dupuytren's disease, it is characteristic that the fingers, usually the ring finger and the little finger, contract towards the palm of the hand.
In both cases, low-dose radiation therapy is applied to the affected areas to reduce the formation and growth of nodules and fibrous bands. Radiation acts by interfering with the proliferation process of fibroblasts, which are the cells responsible for the formation of fibrous tissue. By decreasing the activity of these fibroblasts, radiation therapy helps prevent disease progression and can reduce the size and stiffness of existing contractures. This treatment is most effective in the early stages of both diseases, when the tissue has not yet completely hardened.
And you, do you know more uses of radiotherapy?


4 comments
Me encanta el artículo. He descubierto usos de la radioterapia que no conocía, es muy interesante.
Que interesante, no sabia mucho de este tema y me ha sido entender, gracias espero q publiquen más temas relacionados
Que interesante, no sabia mucho de este tema y me ha sido entender, gracias espero q publiquen más temas relacionados
Otro tema muy innovador para mí y muy interesante.
Fácil de lectura y comprensión.Graciasssss